Use physical drives on Linux VirtualBox 7

Sometimes, you might want to use a physical disk on a VM.
In this article, we will go through all steps necessary to mount a physical drive into your VirtualBox VM on Linux.
First, once you have plugged your USB drive (or connected the drive to a SATA port), open a terminal:
sudo lshw -class disk
You will get a result like this: (The data you have to look for are highlighted in red)
sudo password for user:
*-disk:0
description: SCSI Disk
product: 2.0 Reader -0
vendor: Generic
physical id: 0.0.0
bus info: scsi@6:0.0.0
logical name: /dev/sdc
version: 1.00
capabilities: removable
configuration: logicalsectorsize=512 sectorsize=512
*-medium
physical id: 0
logical name: /dev/sdc
*-disk:1
description: ATA Disk
product: CT480BX500SSD1
physical id: 0.0.0
bus info: scsi@3:0.0.0
logical name: /dev/sdb
version: 054
serial: 2203E5FE03CE
size: 447GiB (480GB)
capabilities: gpt-1.00 partitioned partitioned:gpt
configuration: ansiversion=5 guid=44c2d0dc-751c-4a8f-88df-c615bea9199c logicalsectorsize=512 sectorsize=512
Look for the logical name, in our example, it's /dev/sdb.
Then set the name of your drive and logical name in the command below.
sudo VBoxManage createmedium disk --filename debian.vmdk --format=VMDK \ --variant RawDisk --property RawDrive=/dev/sdb
This will create a file debian.vmdk pointing to your physical drive.
Now start VirtualBox as root otherwise virtualbox will not be able to access the HDD, and create a new VM, then use this file as HDD.
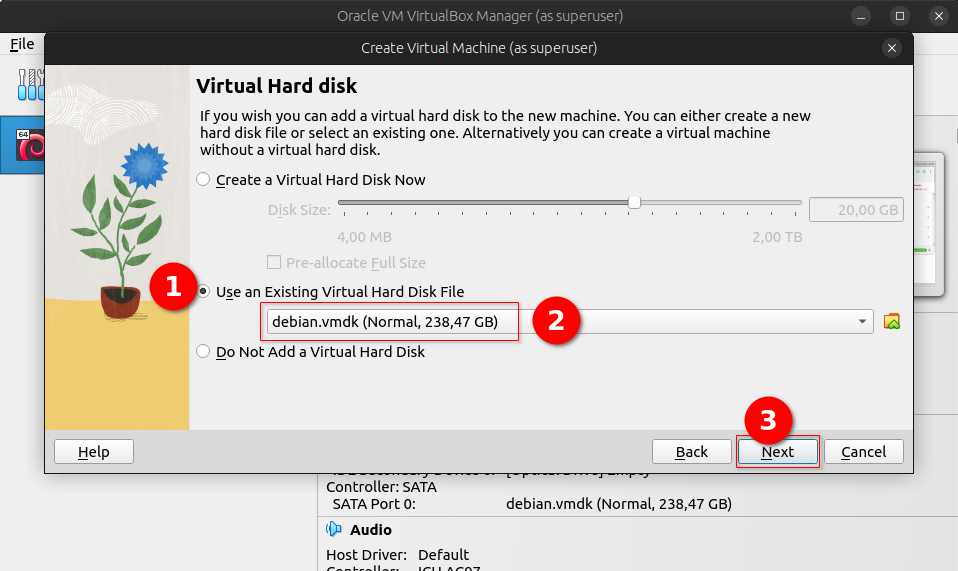
That's it you can now boot the os which is on your physical drive right into your VM, or install a new OS on it to prepare a brand new PC that you don't have yet :-)