Backup Synology DMS7.x on Mega.io
This article will show you how to backup your Synology NAS with DSM7 on Mega.io
We will see how to backup your Synology NAS with DSM7.x on Mega.io
Install mega-cmd
As the package center didn't update the mega package we can't use the package center to install it.
So we will need to install it manually.
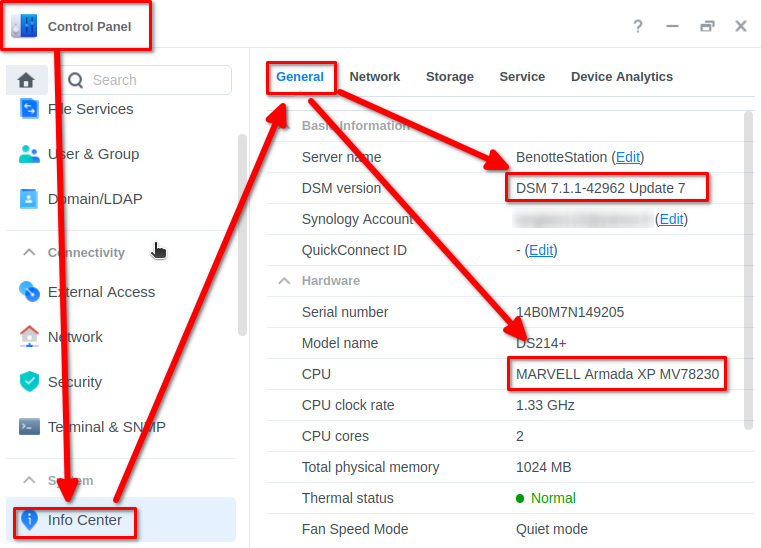
First check what is your DSM version and the architecture of your NAS:
Then we need to download the latest version of mega-cmd tools.
Got to https://mega.io/nas
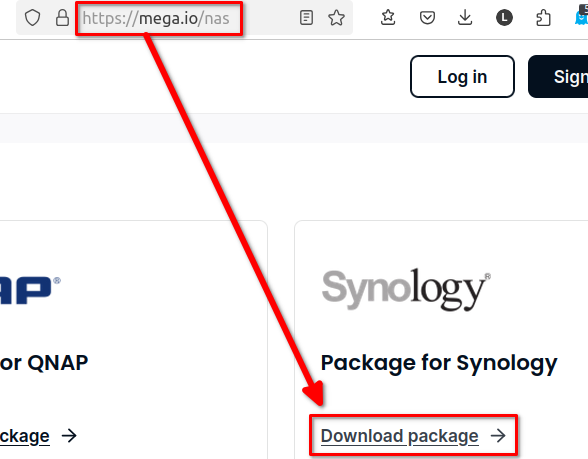
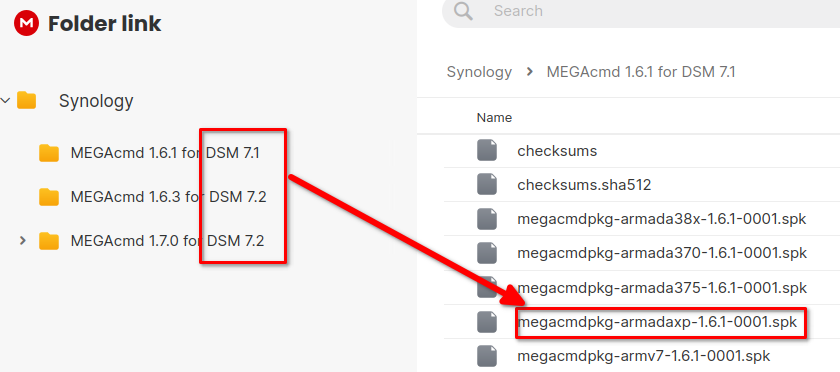
Select the file matching your DSM version and architecture
Login to your DSM web interface then open Package center > Manual Install
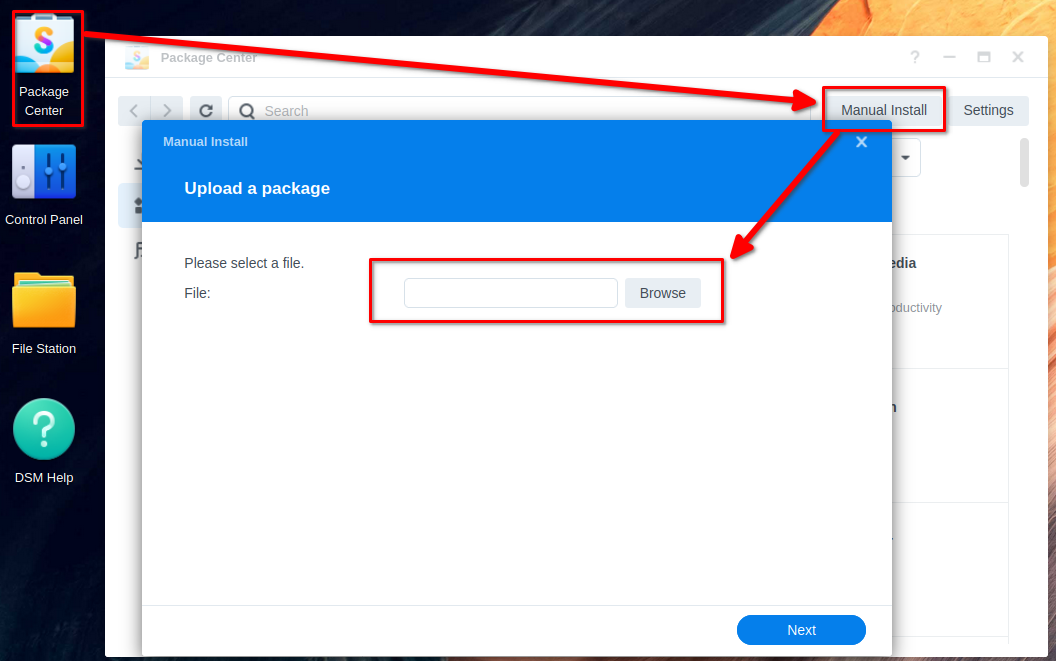
Select the package you just download then click on next and Install
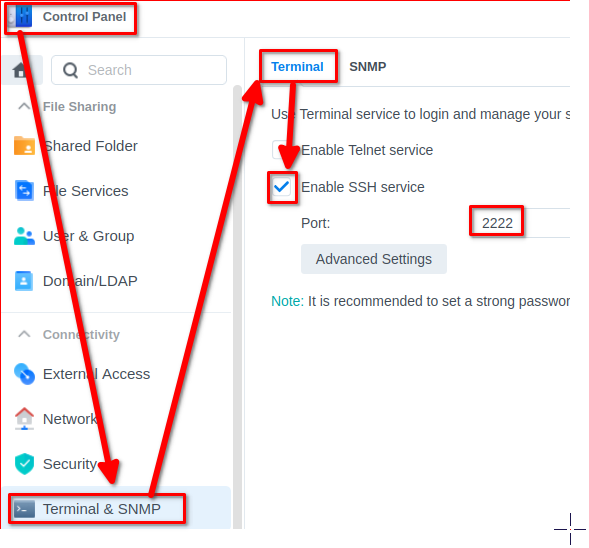
Enable SSH
Once installed, make sure the ssh service is enable.
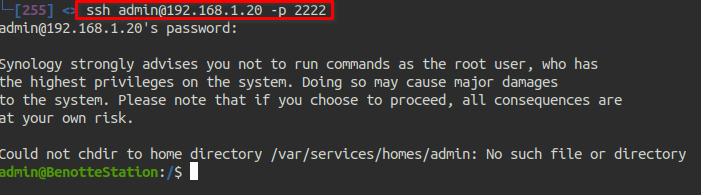
Then login to your NAS using ssh:
Authenticate to mega.io
The first thing we need to authenticate the mega service with our Mega.io account:
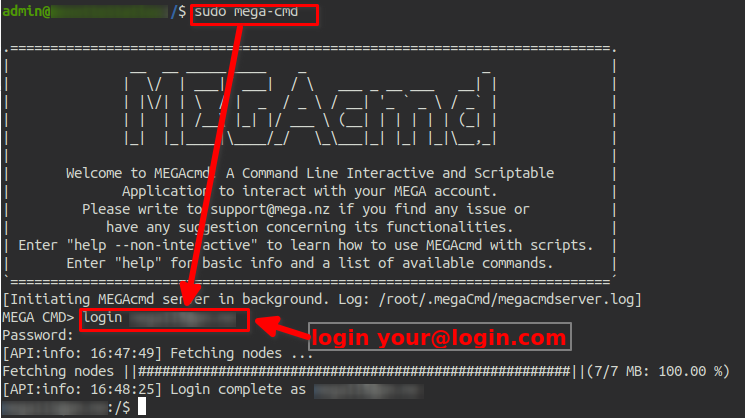
When you type a sudo command for the first time, it will ask you for the admin password.
You are now logged in your mega account. You can verify this by typing ls command.
In my case I have created a synology folder at the root of my mega account:
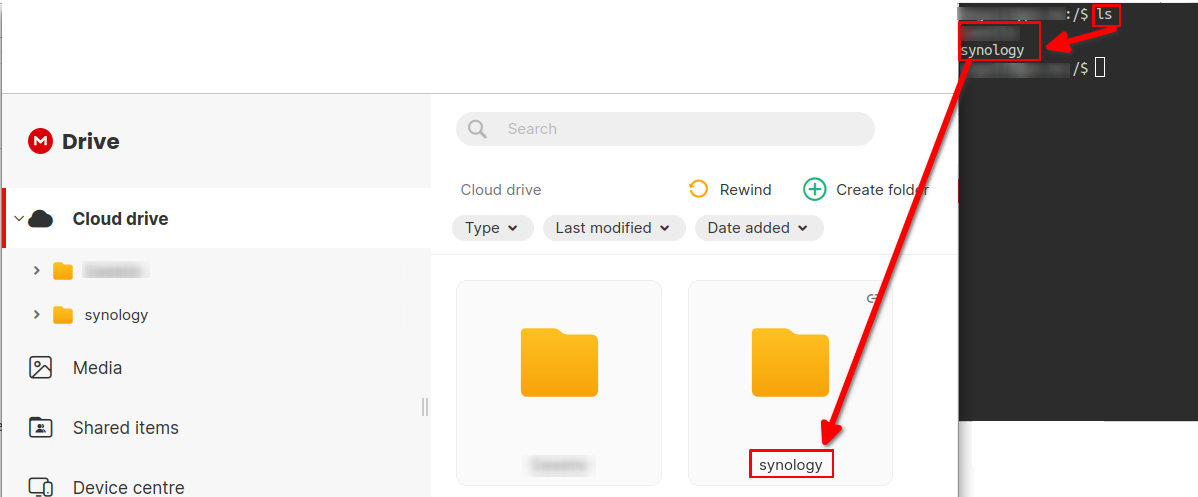
Once you've done that you can quit the mega cli by typing exit
Schedule a backup
Now I want to backup the content of my NAS folder /Backup/My_Backup to the /synology folder on mega.io.
To do this we will use mega-backup command like so:
sudo mega-backup /volume1/Backup/My_Backup /synology --period="0 0 1 * * *" --num-backups=2
This will create a backup of /Backup/My_Backup from my synology NAS to the /synology folder on mega.io.
Hint: Don't forget to add /volume1 in front of the path you want to backup, this is where your NAS save all your files.
You can use sudo mega-backup -l to list your scheduled backup
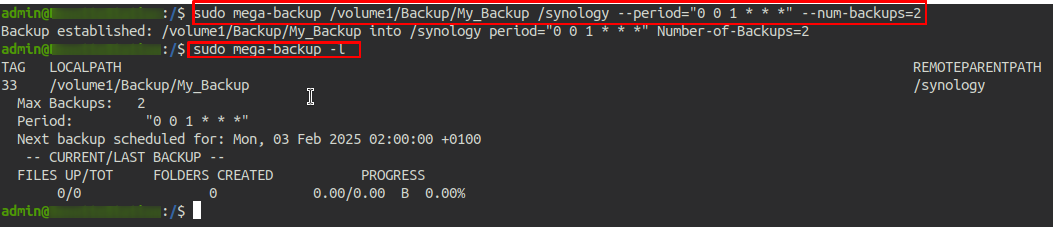
Remove a scheduled backup
To remove a backup schedule, use sudo mega-backup -d <TAG ID>
In this exemple the tag ID would be 33
Get help
For more information on the command mega-backup use sudo mega-backup --help this will give you the following:
Usage: backup (localpath remotepath --period="PERIODSTRING" --num-backups=N | [-lhda] [TAG|localpath] [--period="PERIODSTRING"] [--num-backups=N]) [--time-format=FORMAT]
Controls backups
This command can be used to configure and control backups.
A tutorial can be found here: https://github.com/meganz/MEGAcmd/blob/master/contrib/docs/BACKUPS.md
If no argument is given it will list the configured backups
To get extra info on backups use -l or -h (see Options below)
When a backup of a folder (localfolder) is established in a remote folder (remotepath)
MEGAcmd will create subfolder within the remote path with names like: "localfoldername_bk_TIME"
which shall contain a backup of the local folder at that specific time
In order to configure a backup you need to specify the local and remote paths,
the period and max number of backups to store (see Configuration Options below).
Once configured, you can see extended info asociated to the backup (See Display Options)
Notice that MEGAcmd server need to be running for backups to be created.
Display Options:
-l Show extended info: period, max number, next scheduled backup
or the status of current/last backup
-h Show history of created backups
Backup states:
While a backup is being performed, the backup will be considered and labeled as ONGOING
If a transfer is cancelled or fails, the backup will be considered INCOMPLETE
If a backup is aborted (see -a), all the transfers will be canceled and the backup be ABORTED
If MEGAcmd server stops during a transfer, it will be considered MISCARRIED
Notice that currently when MEGAcmd server is restarted, ongoing and scheduled transfers
will be carried out nevertheless.
If MEGAcmd server is not running when a backup is scheduled and the time for the next one has already arrived,
an empty BACKUP will be created with state SKIPPED
If a backup(1) is ONGOING and the time for the next backup(2) arrives, it won't start untill the previous one(1)
is completed, and if by the time the first one(1) ends the time for the next one(3) has already arrived,
an empty BACKUP(2) will be created with state SKIPPED
--path-display-size=N Use a fixed size of N characters for paths
--time-format=FORMAT show time in available formats. Examples:
RFC2822: Example: Fri, 06 Apr 2018 13:05:37 +0200
ISO6081: Example: 2018-04-06
ISO6081_WITH_TIME: Example: 2018-04-06T13:05:37
SHORT: Example: 06Apr2018 13:05:37
SHORT_UTC: Example: 06Apr2018 13:05:37
CUSTOM. e.g: --time-format="%Y %b": Example: 2018 Apr
You can use any strftime compliant format: http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/ctime/strftime/
Configuration Options:
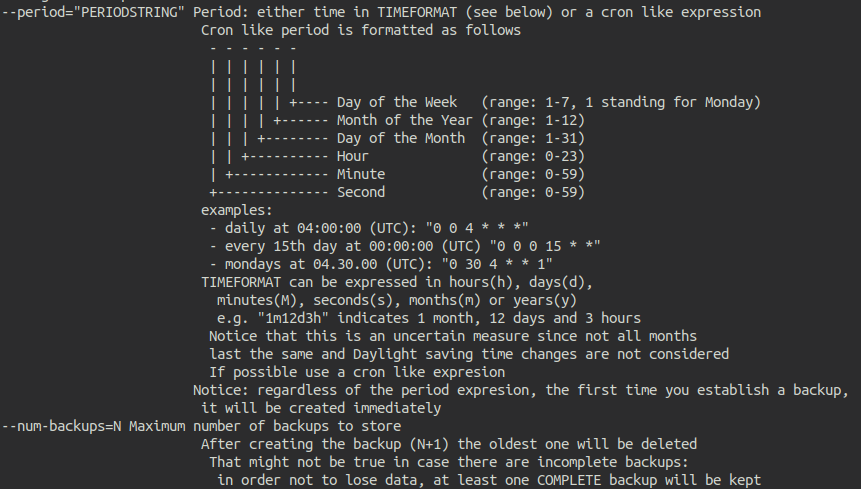
--period="PERIODSTRING" Period: either time in TIMEFORMAT (see below) or a cron like expression
Cron like period is formatted as follows
- - - - - -
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | +---- Day of the Week (range: 1-7, 1 standing for Monday)
| | | | +------ Month of the Year (range: 1-12)
| | | +-------- Day of the Month (range: 1-31)
| | +---------- Hour (range: 0-23)
| +------------ Minute (range: 0-59)
+-------------- Second (range: 0-59)
examples:
- daily at 04:00:00 (UTC): "0 0 4 * * *"
- every 15th day at 00:00:00 (UTC) "0 0 0 15 * *"
- mondays at 04.30.00 (UTC): "0 30 4 * * 1"
TIMEFORMAT can be expressed in hours(h), days(d),
minutes(M), seconds(s), months(m) or years(y)
e.g. "1m12d3h" indicates 1 month, 12 days and 3 hours
Notice that this is an uncertain measure since not all months
last the same and Daylight saving time changes are not considered
If possible use a cron like expresion
Notice: regardless of the period expresion, the first time you establish a backup,
it will be created immediately
--num-backups=N Maximum number of backups to store
After creating the backup (N+1) the oldest one will be deleted
That might not be true in case there are incomplete backups:
in order not to lose data, at least one COMPLETE backup will be kept
Use backup TAG|localpath --option=VALUE to modify existing backups
Management Options:
-d TAG|localpath Removes a backup by its TAG or local path
Folders created by backup won't be deleted
-a TAG|localpath Aborts ongoing backup
Caveat: This functionality is in BETA state. If you experience any issue with this, please contact: support@mega.nz